What is urticaria?
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a skin disease characterised by the appearance of an itchy rash formed by wheals.
Urticaria affects approximately 20% of the world’s population at some point in their life (1).
Some forms of urticaria are elicited by external or internal triggering factors, e.g. cold, sun, or exercise. This type of urticaria is termed ‘inducible urticaria’, whereas the diagnosis ‘chronic spontaneous urticaria’ (CSU) covers urticaria patients where the symptoms occur without a known trigger and last for more than 6 weeks.
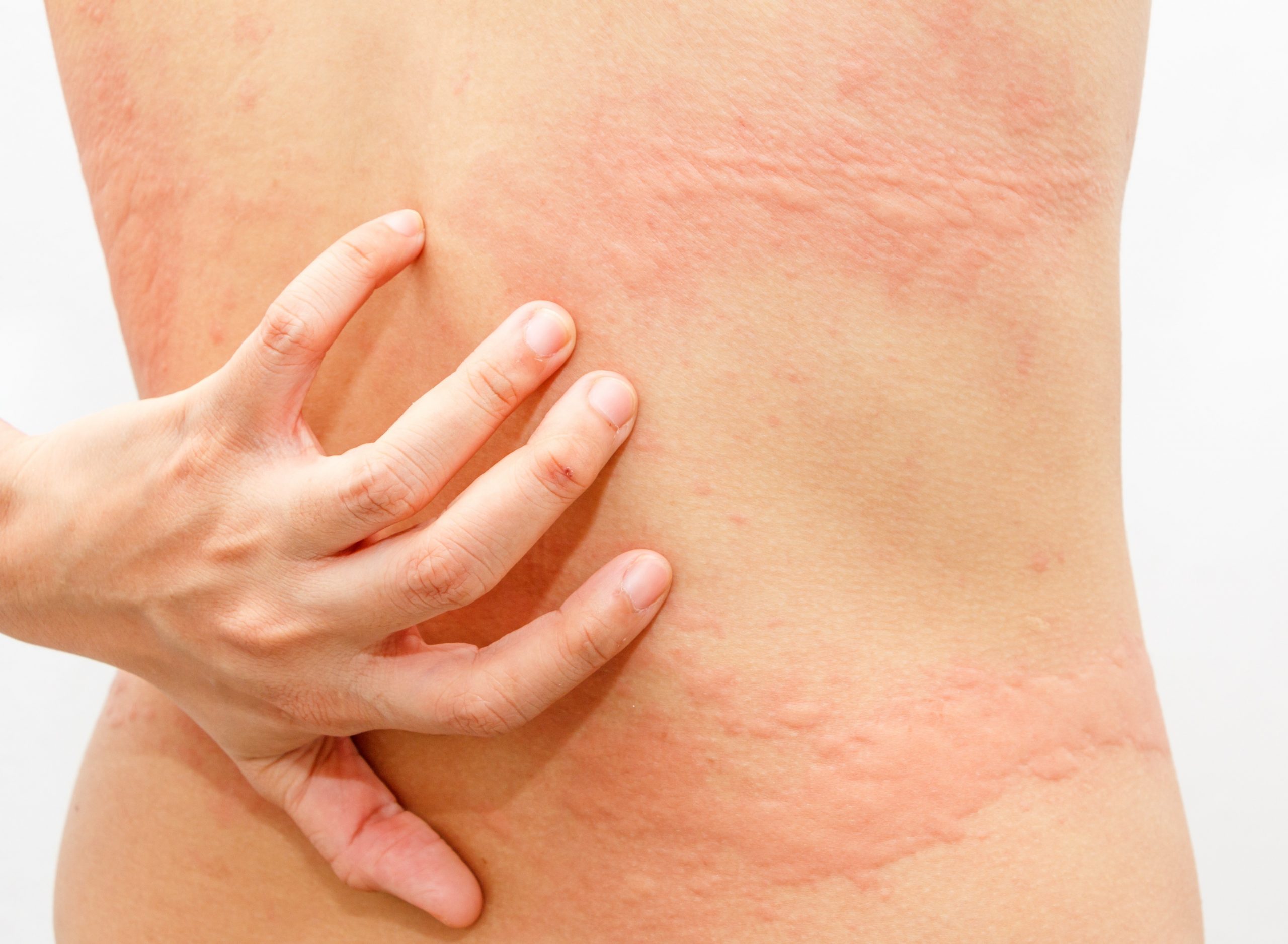
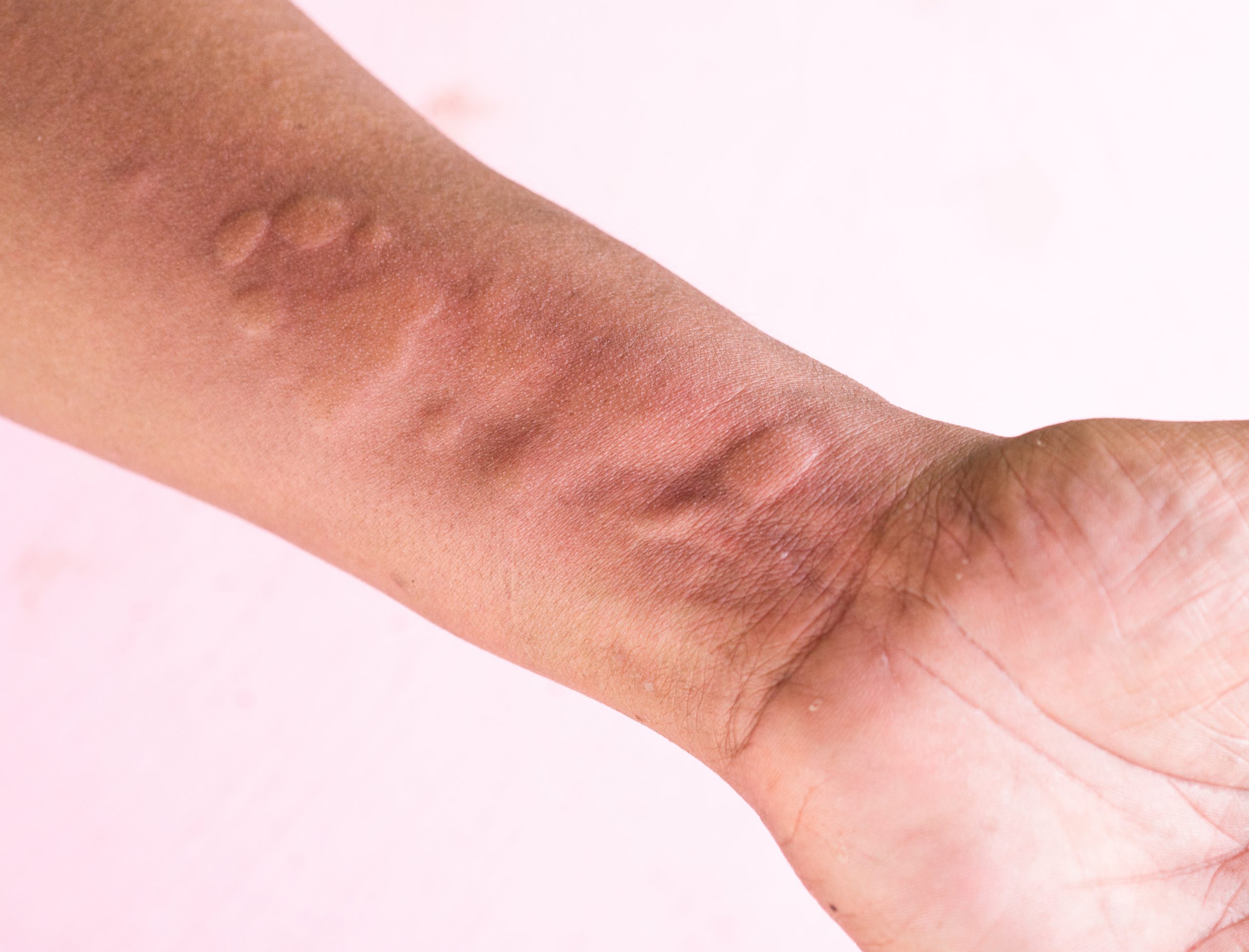
What is CHRONIC SPONTANEOUS URTICARIA (CSU)?
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is a severely debilitating type of urticaria affecting up to 1% of the population worldwide. Living with CSU implies a significantly greater negative impact on the patients’ quality of life compared to any other skin disease (2,3).
Underdiagnosis is frequent and many patients are not treated according to the guidelines. This results in high rates of health care usage and work impairment (4). The underlying disease mechanisms are still not fully known and reliable predictors of disease severity, prognosis, and treatment efficacy are lacking. This is particularly critical due to the high frequency of incomplete treatment responses observed amongst CSU patients (1,5).
CSU is an autoimmune disease which falls into two categories, type I and type IIb, based on the immunological hypersensitivity reaction pattern (6).
- Type I is caused by the production of IgE directed against self-antigens; so-called autoallergens
- Type IIb is linked to the formation of IgG autoantibodies recognizing receptor-bound IgE or the high-affinity IgE receptor (FcεRI) itself (6)
Common to both subtypes are the activation of mast cells. Mast cells are the key drivers of the disease, which enables release of mediators such as histamine (7). In general, CSU patients classified as type IIb have more severe disease compared to type I. These patients are typically less responsive to the first line therapy, antihistamines, and will have a slower or no response to the currently available biological treatment, omalizumab (8).
Urticaria testing provided by RefLab
The differences between CSU patients makes it important to diagnose the patients correctly to provide them with the optimal medical care.
In vitro basophil activation tests are currently used to screen for autoreactive autoantibodies against IgE or FcεRI, as basophils, like mast cells, also express the IgE receptor and react to receptor cross-linking by releasing histamine. The basophils are thus mimicking the response from mast cells in vivo (9,10).

RefLab provides the only accredited laboratory assay to test for autoreactive occurring in type IIb CSU ; the serum-induced basophil histamine release assay (s-BHRA). The test is performed in RefLabs own laboratory for children as well as adults by sending a serum sample to RefLab. The test result is provided within 7-21 business days.
